Applications of binary trees
- Binary Search Tree - Used in many search applications where data is constantly entering/leaving, such as the map and set objects in many languages' libraries.
- Binary Space Partition - Used in almost every 3D video game to determine what objects need to be rendered.
- Binary Tries - Used in almost every high-bandwidth router for storing router-tables.
- Hash Trees - used in p2p programs and specialized image-signatures in which a hash needs to be verified, but the whole file is not available.
- Heaps - Used in implementing efficient priority-queues, which in turn are used for scheduling processes in many operating systems, Quality-of-Service in routers, and A* (path-finding algorithm used in AI applications, including robotics and video games). Also used in heap-sort.
- Huffman Coding Tree (Chip Uni) - used in compression algorithms, such as those used by the .jpeg and .mp3 file-formats.
- GGM Trees - Used in cryptographic applications to generate a tree of pseudo-random numbers.
- Syntax Tree - Constructed by compilers and (implicitly) calculators to parse expressions.
- Treap - Randomized data structure used in wireless networking and memory allocation.
- T-tree - Though most databases use some form of B-tree to store data on the drive, databases which keep all (most) their data in memory often use T-trees to do so.
#Source from Stack Overflow
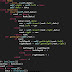
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.right = self.left = None
self.data = data
class Solution:
def insert(self,root,data):
if root == None:
return Node(data)
else:
if data<=root.data:
cur = self.insert(root.left,data)
root.left = cur
else:
cur = self.insert(root.right,data)
root.right = cur
return root
def getHeight(self,root):
if root:
leftDepth = self.getHeight(root.left)
rightDepth = self.getHeight(root.right)
if leftDepth > rightDepth:
return leftDepth + 1
else:
return rightDepth + 1
else:
return -1
T= int(input())
myTree = Solution()
root = None
for i in range(T):
data = int(input())
root = myTree.insert(root,data)
height = myTree.getHeight(root)
print(height)
Applications of Binary Search Trees
 Reviewed by Akhil Kumar
on
July 08, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Akhil Kumar
on
July 08, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Akhil Kumar
on
July 08, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Akhil Kumar
on
July 08, 2019
Rating:









No comments: